Wireless Infrastructure

Microwave-assisted chemical synthesis has garnered significant interest in recent years due to its ability to expedite reaction times, reduce energy consumption, and provide environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional methods. Since the first reports of using microwaves for chemical synthesis in the 1980s, technology has evolved dramatically, opening new avenues for innovation in green chemistry and industrial applications.
According to Springer the global market for microwave-assisted synthesis is projected to reach $3.5 billion by 2027, driven by demand in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and sustainability applications, where the demand for faster, more efficient, and sustainable chemical processes is rapidly expanding. Discover the principles of microwave driven chemical reactions and see the potential of RFHIC’s GaN solid-state microwave solutions can be utilized for next generation chemical synthesis applications.
Principles of Microwave Technology in Chemical Reactions
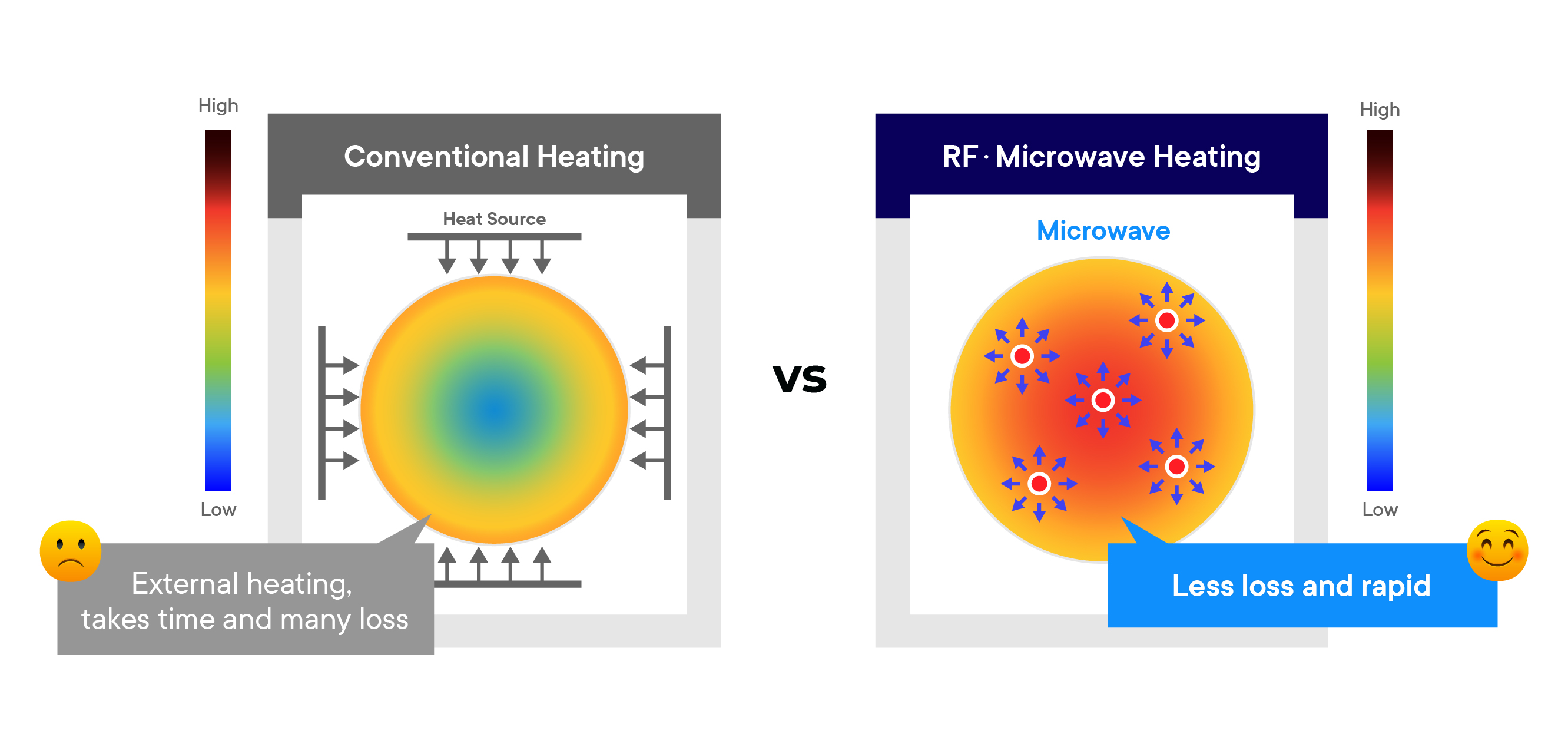
Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation with frequencies ranging from 300 MHz to 300 GHz. When applied to chemical reactions, microwaves primarily interact with polar molecules, inducing rapid molecular rotations and vibrations. This process generates heat, which accelerates chemical reactions by providing the necessary activation energy (Ea) more efficiently than conventional methods.
The fundamental difference between microwave heating and traditional heating lies in how energy is transferred. In conventional methods, heat is transferred from an external source to the reactants via conduction and convection. However, microwave irradiation interacts directly with the molecules, allowing for volumetric heating, which significantly enhances reaction rates. Studies have shown that microwave energy can decrease the Ea of certain reactions, leading to more efficient conversion rates and lower operational temperatures.
Applications of Microwave-Assisted Synthesis
Microwave-assisted synthesis is used in a wide variety of chemical processes, ranging from organic synthesis to materials science. The technology has demonstrated significant advantages in reactions such as:

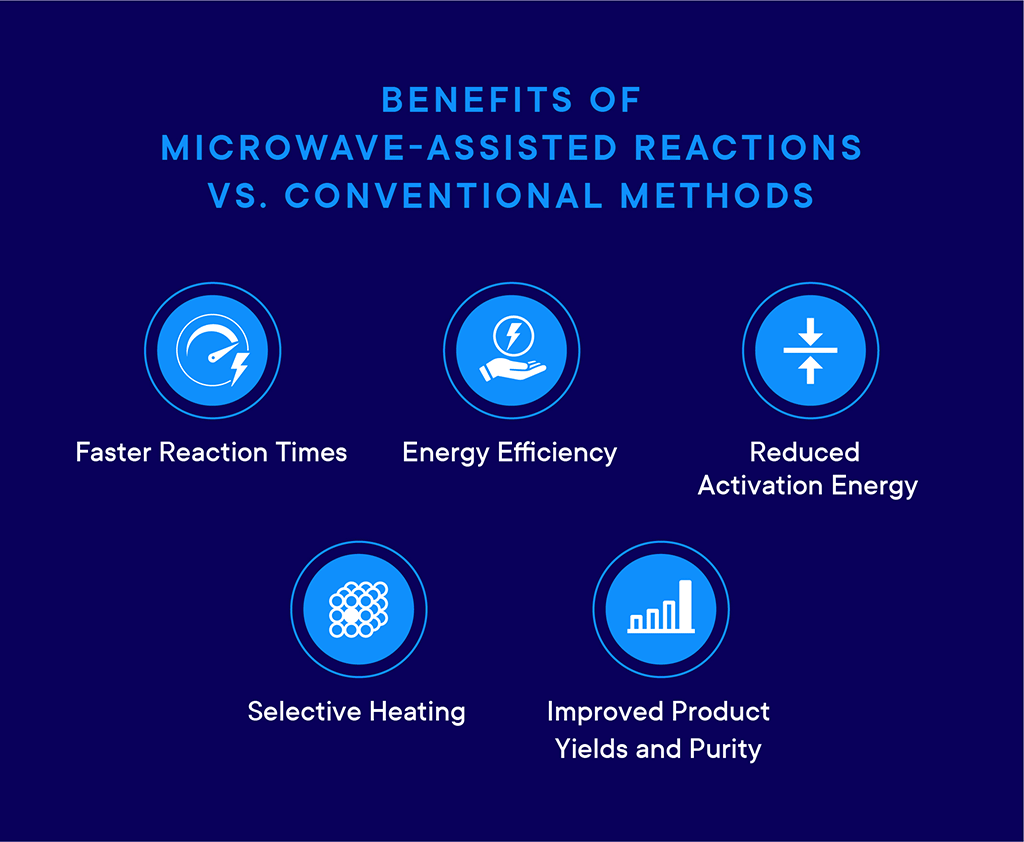
Benefits of Microwave-Assisted Reactions vs. Conventional Methods
RFHIC’s GaN Solid-State Microwave Technology for Green Chemistry
RFHIC's gallium nitride (GaN) solid-state microwave technology presents a promising solution for overcoming some of the limitations of conventional microwave-assisted synthesis.
RFHIC’s GaN solid-state amplifiers provide several advantages over traditional heating systems, including:
1. Higher Efficiency: GaN devices offer higher electrical efficiency compared to traditional heating sources, converting more input power into microwave energy. This results in lower energy consumption and reduces operating costs, making it an ideal choice for sustainable chemistry applications.
2. Precise Power Control: Unlike conventional heating technologies, GaN solid-state amplifiers allow for precise control over microwave power and frequency. This level of control enables fine-tuning of reaction conditions, improving yields and reducing by-products.
3. Scalability: GaN technology is highly scalable, making it suitable for both small-scale laboratory experiments and large-scale industrial processes. Its ability to operate at higher frequencies and power levels also expands the range of possible chemical reactions.
4. Enhanced Stability and Lifetime: GaN devices have long operational lifetimes upto 50,000 to 100,000 hours. This makes them more reliable for continuous operation in industrial environments.
Future of Microwave-Assisted Green Chemistry
As industries continue to seek greener and more efficient processes, the adoption of microwave-assisted chemical synthesis is expected to grow. The combination of microwave technology with advanced catalysts and renewable energy sources could revolutionize industries such as pharmaceuticals, materials science, and environmental remediation.
By leveraging RFHIC's GaN solid-state microwave systems, industries can further enhance the efficiency and sustainability of their processes. GaN technology offers a versatile, scalable, and energy-efficient solution for implementing microwave-driven reactions in industrial-scale green chemistry applications. As industries seek to reduce their environmental impact, RFHIC's GaN microwave solutions provide a robust, scalable, and sustainable option for the future of chemical synthesis
If you would like to learn more about our GaN solid-state microwave offerings, please complete the form below.
References
1. Zhou, J. et al. "A New Type of Power Energy for Accelerating Chemical Reactions: The Nature of a Microwave-Driving Force for Accelerating Chemical Reactions." Scientific Reports, 2016.
2. Nüchter, M., Ondruschka, B., Bonrath, W., & Gumb, A. "Microwave-Assisted Synthesis: A Critical Technology Overview." Green Chemistry, 2004.